Optive Plus UD
OPTIVE PLUS™ UD features a unique triple-action formula designed to provide long-lasting comfort.
OPTIVE PLUS™ UD lubricates the surface of the eye and moisturises ocular surface cells by restoring osmotic balance, while also helping protect natural tears through lipid enhancement. It is classified as a second-line, medium-viscosity eye drop.
OPTIVE PLUS™ UD is used in the treatment of lipid-deficient dry eye. Its triple-action formulation helps provide symptomatic relief by reducing tear evaporation.
Innovative technology
Lipid based tears:
Helps soothe dry eye symptoms.
Replaces the deficient lipid layer.
Carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) Based Tears:
Provides lasting comfort and lubrication.
Supports a long retention time on the ocular surface.
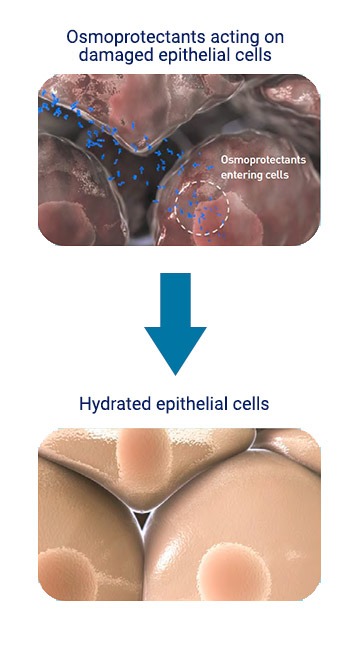
Osmoprotection Based Tears:
Provides surface hydration.
Protects against hyperosmotic stress.
Helps restore osmotic balance.
Instillation
Instil one or two drops of OPTIVE PLUS™ UD into the affected eye(s) as needed.
When used for postoperative care, it is important to follow the advice provided by the prescribing eye care practitioner.
Ingredients
OPTIVE PLUS™ UD is supplied in unit dose vials containing 0,4ml.
Precautions
Add-on treatment
Higher-viscosity OPTIVE® GEL DROPS are an effective add-on treatment to OPTIVE PLUS™ UD, providing long-lasting relief both during the day and at night.
OPTIVE PLUS™ Eye Drops and OPTIVE PLUS™ Unit Dose Eye Drops: Contains carboxymethylcellulose sodium 5 mg/ml, glycerine 10 mg/ml, castor oil 2,5 mg/ml, and polysorbate 80 5 mg/ml.
OPTIVE® Gel Drops: Contains carboxymethylcellulose sodium 10 mg/ml and glycerine 9 mg/ml.
For full prescribing information, refer to the Instructions for Use.
Allergan Pharmaceuticals (Pty) Ltd, PO Box 6024, Halfway House, 1685, South Africa (Co. Reg. no. 1984/005576/07)
Telephone: +27 (0) 11 545 6600, Facsimile: +27 (0) 11 315 6008
www.allergan.co.za
© 2018. ®/™ Registered Trademark/Trademark of Allergan, Inc. ZA/0104/2018c
Clinical References
1. Allergan South Africa.
2. Allergan Australia.
3. Optive UK. https://www.allerganaesthetics.co.uk/
4. DEWS. Definition and Classifications Subcommittee. Ocul Surf. 2007;5(2):75-92.
5. Abelson MB. Code red: the key features of hyperemia. RevOphthalmol. Published April 22, 2010. (Accessed August 28, 2014).
6. Kent C. Managing and making sense of MGD. RevOphthalmology. Published October 4, 2012. (Accessed August, 2014).